Windows Blue Screen Fix: A Complete Guide
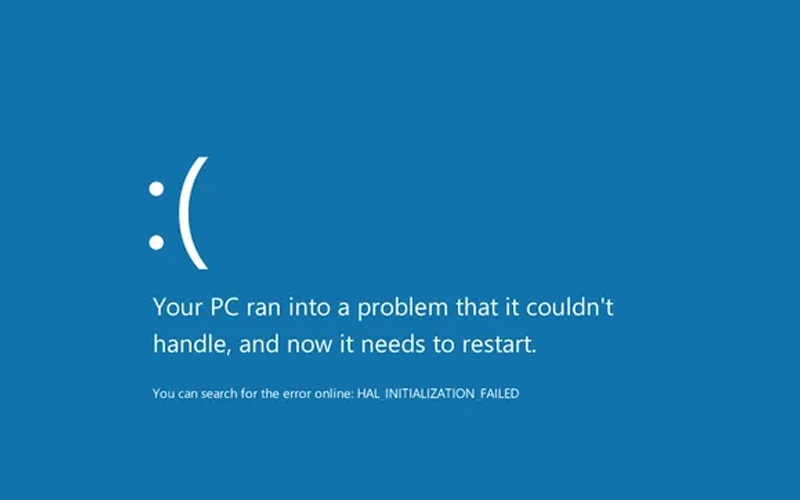
The infamous “Blue Screen of Death” (BSOD) is a common issue for Windows users. While it can be alarming, understanding the causes and solutions can help you restore your system’s stability quickly.
1. What Is the Blue Screen of Death?
A Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) occurs when Windows encounters a critical error it cannot recover from. It usually displays an error message and a stop code, providing clues to the root cause.
Common BSOD Stop Codes:
- CRITICAL_PROCESS_DIED: Indicates a critical system process failed.
- MEMORY_MANAGEMENT: Points to issues with RAM or virtual memory.
- DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL: Signals a faulty driver.
2. Causes of BSOD
Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Common reasons include:
- Hardware Issues: Faulty RAM, overheating, or failing storage devices.
- Software Conflicts: Incompatible drivers or recently installed programs.
- System Updates: Failed updates or incompatible patches.
- Malware: Viruses can corrupt system files, leading to crashes.
3. Step-by-Step Solutions for Fixing BSOD
Step 1: Note the Error Code
- When the BSOD occurs, write down the stop code or take a picture.
- Search the stop code online to narrow down possible causes.
Step 2: Boot into Safe Mode
- Restart your computer and press F8 (or hold Shift while selecting Restart).
- Choose Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Startup Settings > Enable Safe Mode.
- In Safe Mode, only essential drivers and services are loaded, allowing you to isolate the problem.
Step 3: Check for Recent Changes
-
Uninstall Problematic Updates or Software:
- Go to Control Panel > Programs > Programs and Features.
- Remove recently installed programs.
-
Update Drivers:
- Use Device Manager to identify outdated or faulty drivers.
- Right-click the device, select Update Driver, or download the latest driver from the manufacturer’s website.
Step 4: Run Diagnostics
-
Check Hardware:
- Run Windows Memory Diagnostic:
- Press Windows + R, type
mdsched.exe, and follow the prompts.
- Press Windows + R, type
- Test your storage drive with tools like CrystalDiskInfo or manufacturer-provided utilities.
- Run Windows Memory Diagnostic:
-
Scan for Malware:
- Use Windows Defender or third-party antivirus software to perform a full system scan.
Step 5: Restore or Reset
-
System Restore:
- Go to Control Panel > Recovery > Open System Restore.
- Select a restore point before the BSOD started.
-
Reset Windows:
- If issues persist, consider resetting Windows while keeping your files:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery > Reset this PC.
- If issues persist, consider resetting Windows while keeping your files:
4. Preventing Future BSOD Issues
-
Keep Software Updated:
- Regularly update Windows and drivers to patch vulnerabilities.
-
Monitor Hardware Health:
- Ensure proper cooling and regularly check for hardware wear.
-
Use Reliable Software:
- Avoid untrusted programs and use antivirus protection.
-
Backup Regularly:
- Use cloud services or external drives to keep critical data safe.
5. When to Seek Professional Help
If you’ve tried the above steps and the BSOD persists, it may be time to consult a professional technician. They can perform advanced diagnostics to identify hardware failures or system corruption.
Conclusion
The Blue Screen of Death may seem intimidating, but with the right approach, you can diagnose and fix most issues. By following these steps and implementing preventive measures, you can ensure a more stable and reliable Windows experience.
Have a specific BSOD stop code or problem?
Skillio: Empowering users with practical solutions to everyday tech challenges.